Best Practice 3
Implicit dependencies should be used whenever possible (see this article from terraform.io website for more information). In this article we will perform the following action with implicit dependencies and with explicit dependencies :
- Create 1 load balancer
- Create 2 network interfaces and link them to a load balancer
Prerequisite
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Azure Subscription | An Azure subscription id |
| Resource Group | An Azure resource group is available |
| Storage Account | An Azure storage account is available and is located in the upper resource group, it contains a container named tfstate |
| Service Principal | An Azure service principal is available and has the owner privilege on the upper resource group |
| Terraform file | Clone this repository and fill in the following files with the upper prerequisite items : Variable used for the Terraform init : secret/backend-jdld.json Variable used for the Terraform plan and apply : main.tf & main-jdld.tfvars & secret/main-jdld.json |
What should we do?
We will create the upper mentioned element using remote backend (see the previous article BestPractice-1 for more information about remote backend).
Review the code main.tf, as illustrated in the following bracket, the implicit and the explicit methods are highlighted.
module "Az-Vm-Demo" {
source = "JamesDLD/Az-Vm/azurerm"
version = "0.1.2"
sa_bootdiag_storage_uri = data.azurerm_storage_account.bp3.primary_blob_endpoint #(Mandatory)
subnets_ids = module.Az-VirtualNetwork-Demo.subnet_ids #(Mandatory)
linux_vms = {} #(Mandatory)
windows_vms = var.vms #(Mandatory)
#This an implicit dependency
internal_lb_backend_ids = module.Create-AzureRmLoadBalancer-Demo.lb_backend_ids
#This an explicit dependency
#internal_lb_backend_ids = ["/subscriptions/${var.subscription_id}/resourceGroups/infr-jdld-noprd-rg1/providers/Microsoft.Network/loadBalancers/demo-bp3-internal-lb1/backendAddressPools/demo-bp3-internal-bckpool1"]
vm_resource_group_name = data.azurerm_resource_group.bp3.name
vm_prefix = "bp3" #(Optional)
windows_storage_image_reference = var.windows_storage_image_reference #(Optional)
admin_username = var.app_admin
admin_password = var.pass
vm_additional_tags = { bp = "3" } #(Optional)
}
1. Usage
This step ensures that Terraform has all the prerequisites to build your template in Azure.
terraform init -backend-config="secret/backend-jdld.json" -reconfigure
The Terraform plan command is used to create an execution plan. This step compares the requested resources to the state information saved by Terraform and then gives as an output the planned execution. Resources are not created in Azure.
terraform plan -var-file="secret/main-jdld.json" -var-file="variable/main-jdld.tfvars"
If all is ok with the proposal you can now apply the configuration with both methods (implicit and explicit) to track the impact.
terraform apply -var-file="secret/main-jdld.json" -var-file="variable/main-jdld.tfvars"
We will now destroy what we have done with both methods (implicit and explicit) to track the impact.
terraform destroy -var-file="secret/main-jdld.json" -var-file="variable/main-jdld.tfvars"
2. Analysis
| Description | Screenshot |
|---|---|
| Our 2 network interfaces are linked to the Load Balancer | 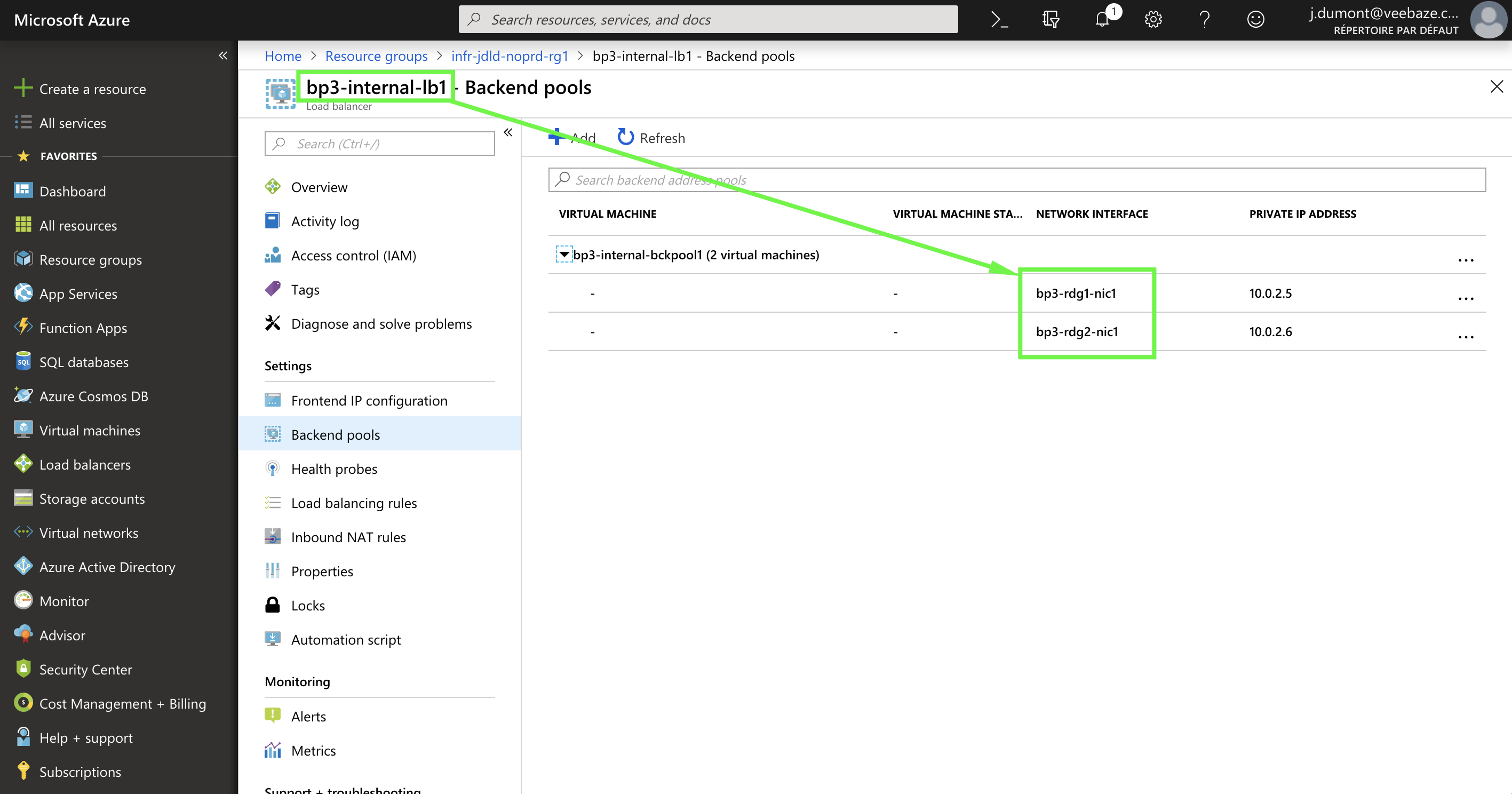 |
| When using implicit dependencies all is working like a charm | 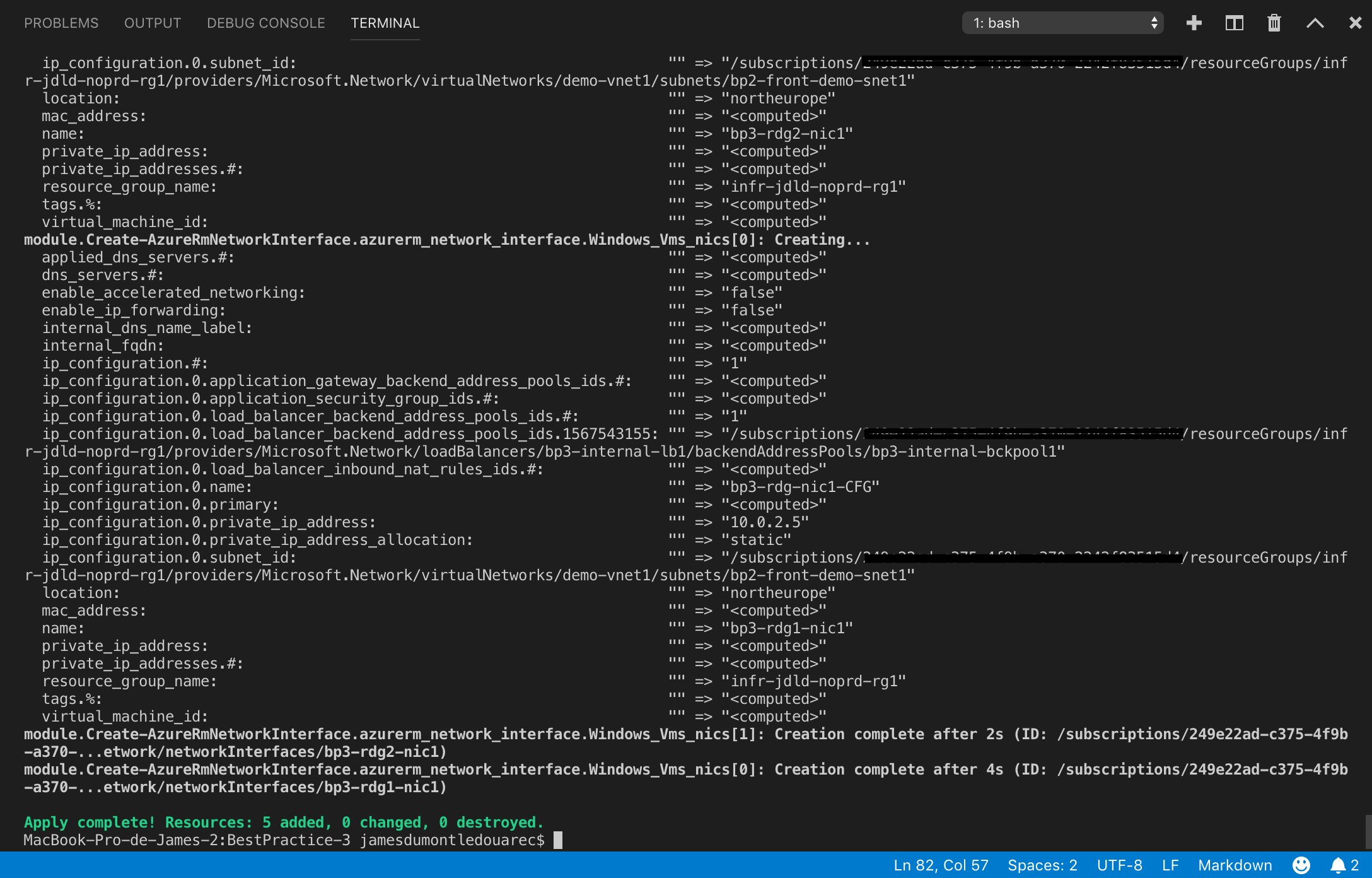 |
| When using explicit dependencies we receive error(s) because some resources doesn’t wait for other to be created (a workaround consists in using the variable depend on but this will still cause error when you will proceed Terraform destroy) |
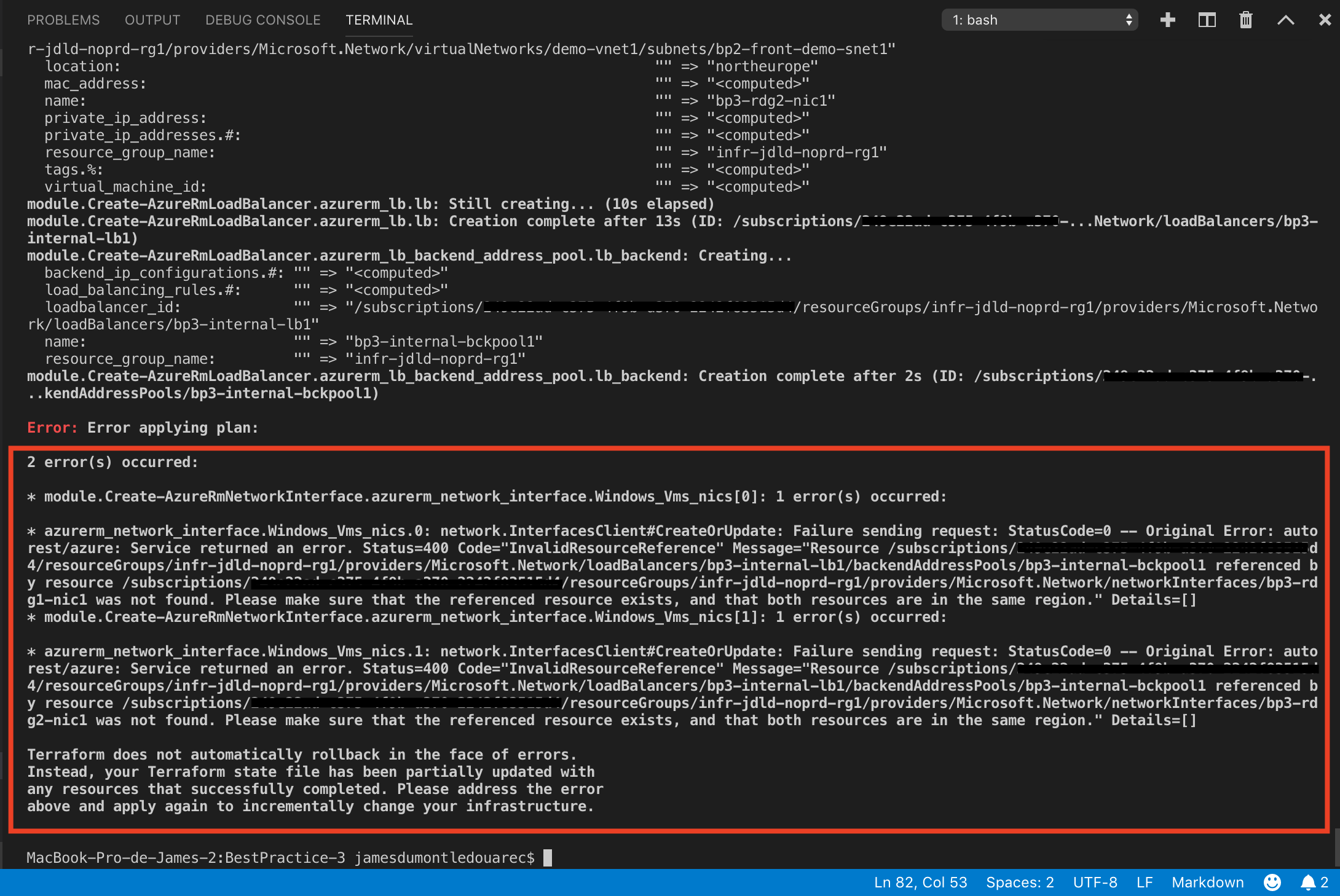 |
See you!
JamesDLD